Equation Layout API Reference
Contents
- EQN_Container
- EQN_Offset
- EQN_Fraction
- EQN_Scale
- EQN_Color
- EQN_Bracket
- EQN_Root
- EQN_Strike
- EQN_Box
- EQN_TouchBox
- EQN_Bar
- EQN_Integral
- EQN_SumOf
- EQN_ProdOf
- EQN_Subscript
- EQN_Superscript
- EQN_SuperscriptSubscript
- EQN_Comment
- EQN_StrikeComment
- EQN_Pad
- EQN_Matrix
- EQN_Lines
- EQN_Annotate
EQN_Container
Equation container options
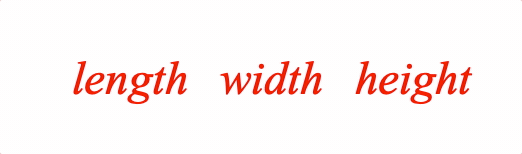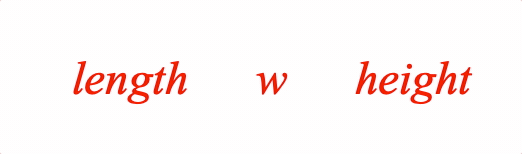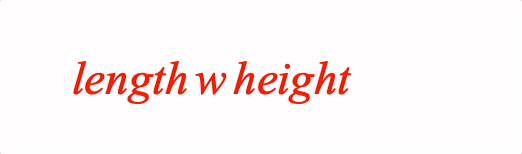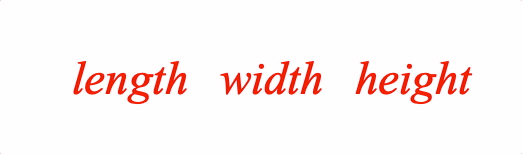
A container is useful to fix spacing around content as it changes between equation forms.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- width: number | undefined = null
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
- descent: number | undefined = null
- ascent: number | undefined = null
- xAlign: 'left' | 'center' | 'right' | number | undefined = 'center'
- yAlign: 'bottom' | 'middle' | 'top' | 'baseline' | number | undefined = 'baseline'
- fit: 'width' | 'height' | 'contain' | undefined = null
- scale: number | undefined = 1
-
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
-
- showContent: boolean | undefined = true
- if
false, a container will be created around the content, but the content will not be shown
Example showing the difference between with and without container
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
// Container object definition
1: [
'length',
{
container: {
content: 'width',
width: 0.5,
},
},
'height',
],
// Container array definition
2: ['length', { container: ['w', 0.5] }, 'height'],
// No container
3: ['length', ' ', 'w', ' ', 'height']
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
Create equation object then add to figure
const eqn = figure.collections.equation({
forms: {
1: [
'length',
{ container: { content: 'width', width: 0.5 } },
'height',
],
2: ['length', { container: ['w', 0.5] }, 'height'],
3: ['length', ' ', 'w', ' ', 'height']
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
figure.add('eqn', eqn);
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Offset
Equation offset options

Offset a phrase from the position it would normally be. An offest phrase will not contribute to layout of subsequent equation elements and phrases.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- offset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
-
Example 1
figure.add([
{
name: 'rect1',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
0: [
'a', '_ = ', 'n',
{ offset: ['for a > 0', [0.3, 0]] },
],
},
},
]);
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Fraction
Equation fraction options
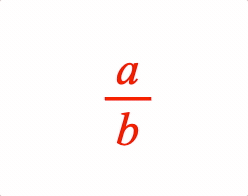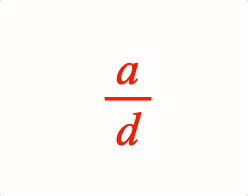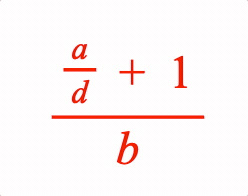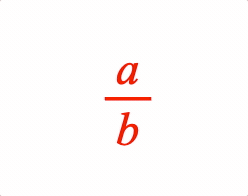
A fraction has a numerator and denominator separated by a vinculum symbol EQN_VinculumSymbol.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- numerator: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string
- Vinculum symbol
- denominator: TypeEquationPhrase
- scale: number | undefined = 1
- numeratorSpace: number | undefined = 0.05
- denominatorSpace: number | undefined = 0.05
- overhang: number | undefined = 0.05
Vinculum extends beyond the content horizontally by the this amount
- offsetY: number | undefined = 0.07
Offset fraction in y
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
Use full bounds with content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { frac: ['a', 'vinculum', 'b'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Example showing object and array fraction definitions, and nesting
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
v1: { symbol: 'vinculum' },
v2: { symbol: 'vinculum' },
plus: ' + ',
},
forms: {
// Fraction object form
1: {
frac: {
numerator: 'a',
denominator: 'b',
symbol: 'v1',
},
},
// Fraction array form
2: { frac: ['a', 'v1', 'd'] },
// Nested
3: {
frac: {
numerator: [{ frac: ['a', 'v1', 'd', 0.7] }, 'plus', '_1'],
symbol: 'v2',
denominator: 'b',
}
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
Create equation object then add to figure
const eqn = figure.collections.equation({
elements: {
v1: { symbol: 'vinculum' },
v2: { symbol: 'vinculum' },
plus: ' + ',
},
forms: {
1: {
frac: {
numerator: 'a',
denominator: 'b',
symbol: 'v1',
},
},
2: { frac: ['a', 'v1', 'd'] },
3: {
frac: {
numerator: [{ frac: ['a', 'v1', 'd', 0.7] }, 'plus', '_1'],
symbol: 'v2',
denominator: 'b',
}
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
figure.add('eqn', eqn);
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Scale
Equation scale
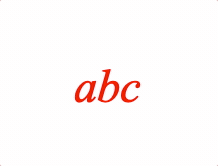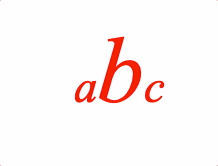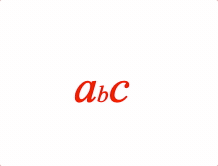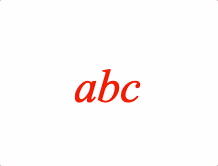
Scale an equation phrase
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- scale: number | undefined = 1
-
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
Use full bounds with content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
2: ['a', { scale: ['b', 2] }, 'c'],
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
// Some different bracket examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
// Default
1: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
// Array definition magnify
2: ['a', { scale: ['b', 2] }, 'c'],
// Object definition shrink
3: [
'a',
{
scale: {
content: ['b', 1],
scale: 0.5,
},
},
'c',
],
// Back to start
4: ['a', { scale: ['b', 1] }, 'c'],
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Color
Equation color
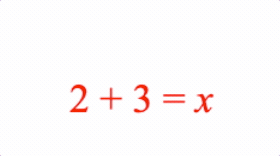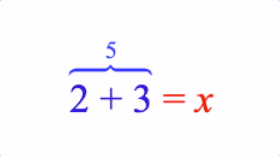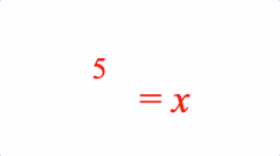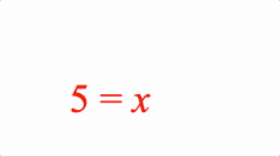
Color an equation phrase.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- color: TypeColor
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
Use full bounds with content
Simple Array Definition
figure.add({
make: 'equation',
forms: {
0: ['a', { color: ['b', [0, 0, 1, 1]] }, 'c'],
},
});
Simple Object Definition
figure.add({
make: 'equation',
forms: {
0: [
'a',
{
color: {
content: 'b',
color: [0, 0, 1, 1],
},
},
'c',
],
},
});
Example 3
figure.add({
make: 'equation',
elements: {
equals: ' = ',
plus: ' + ',
brace: { symbol: 'brace', side: 'top' },
},
forms: {
0: ['2', 'plus', '3', 'equals', 'x'],
1: [
{
color: {
content: { topComment: [['2', 'plus', '3'], '5', 'brace'] },
color: [0, 0, 1, 1],
},
},
'equals', 'x',
],
2: ['5', 'equals', 'x'],
},
touch: { onClick: e => e.nextForm() },
});
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Bracket
Equation bracket
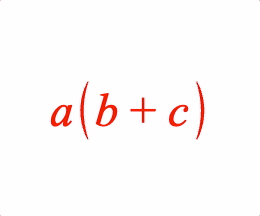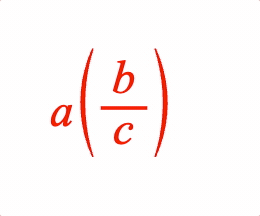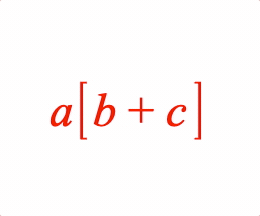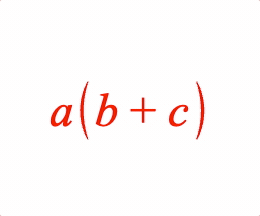
Surround an equation phrase with brackets.
Symbols that can be used with bracket are:
- EQN_BarSymbol
- EQN_ArrowSymbol
- EQN_BraceSymbol
- EQN_BracketSymbol
- EQN_SquareBracketSymbol
- EQN_AngleBracketSymbol
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- left: string | undefined
left bracket symbol
- content: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
- right: string | undefined
right bracket symbol
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes bracket symbols from size of resulting phrase - insideSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space between brackets and content
- outsideSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space between brackets and neighboring phrases
- topSpace: number | undefined = 0.05
how far the brackets extend above the content
- bottomSpace: number | undefined = 0.05
how far the brackets extend below the content
- minContentHeight: number | undefined = null
if content height is less than this, then this number will be used when sizing the brackets (unless it is
null) - minContentDescent: number | undefined = null
if content descent is less than this, then this number will be used when sizing the brackets (unless it is
null) - height: number | undefined = null
force height of brackets
- descent: number | undefined = null
force descent of brackets
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
make: 'equation',
elements: {
lb: { symbol: 'bracket', side: 'left' },
rb: { symbol: 'bracket', side: 'right' },
},
forms: {
1: ['a', { brac: ['lb', ['b', '_ + ', 'c'], 'rb'] }],
},
});
Some different bracket examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
lb: { symbol: 'bracket', side: 'left' },
rb: { symbol: 'bracket', side: 'right' },
lsb: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'left' },
rsb: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'right' },
leftBrace: { }
},
forms: {
// Array definition
1: ['a', { brac: ['lb', ['b', '_ + ', 'c'], 'rb'] }],
// Object definition
2: ['a', {
brac: {
left: 'lb',
content: { frac: ['b', 'vinculum', 'c'] },
right: 'rb',
},
}],
// Square brackets
3: ['a', { brac: ['lsb', ['b', '_ + ', 'c'], 'rsb'] }],
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Root
Equation root
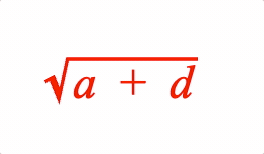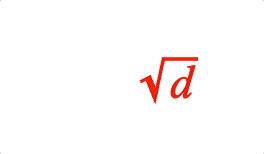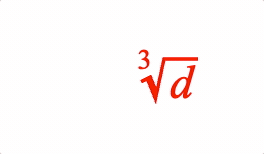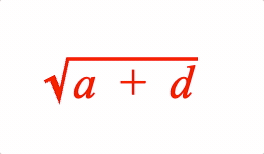
Surround an equation phrase with a radical symbol EQN_RadicalSymbol and add a custom root if needed
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below.
Properties
- symbol: string
radical symbol
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes radical symbol and root (if defined) from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined
(
0.02) default space between content and radical symbol in left, right, top and bottom directions. - topSpace: number | undefined = space
space between content top and radical symbol horiztonal line
- rightSpace: number | undefined = space
radical symbol overhang of content on right
- bottomSpace: number | undefined = space
radical symbol descent below content
- leftSpace: number | undefined = space
space between radical symbol up stroke and content
- root: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
custom root
- rootOffset: number | undefined = [0, 0.06]
custom root offset
- rootScale: number | undefined = 0.6
custom root scale
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { root: ['radical', 'a'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Example showing object and array root definitions, and custom roots
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
r: { symbol: 'radical' },
plus: ' + ',
},
formDefaults: { alignment: { fixTo: 'd' } },
forms: {
// Root object form
1: {
root: {
symbol: 'r',
content: ['a', 'plus', 'd'],
},
},
// Root array form
2: { root: ['r', 'd'] },
// Cube root
3: { root: { content: 'd', symbol: 'r', root: '_3' } },
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
Create equation object then add to figure
const eqn = figure.collections.equation({
elements: {
r: { symbol: 'radical' },
plus: ' + ',
},
formDefaults: {
alignment: { fixTo: 'd' },
},
forms: {
1: {
root: {
symbol: 'r',
content: ['a', 'plus', 'd'],
},
},
2: { root: ['r', 'd'] },
3: { root: { content: 'd', symbol: 'r', root: '_3' } },
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
figure.add('eqn', eqn);
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Strike
Equation strike-through
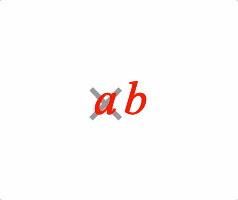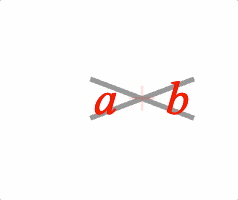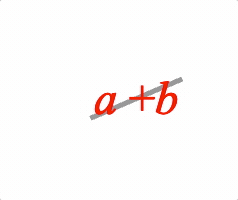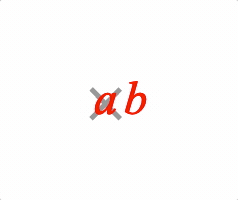
Overlay a strike symbol on an equation phrase.
Use with EQN_Strike symbol.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string
- inSize: boolean | undefined = false
falseexcludes strike symbol from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined = 0.02
amount the strike symbol overhangs the content on the left, right, bottom and top sides
- topSpace: number | undefined = space
use when top overhang between content and strike should be different thant
spaceproperty - rightSpace: number | undefined = space
use when right overhang between content and strike should be different thant
spaceproperty - bottomSpace: number | undefined = space
use when bottom overhang between content and strike should be different thant
spaceproperty - leftSpace: number | undefined = space
use when left overhang between content and strike should be different thant
spaceproperty - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
x: { symbol: 'strike', color: [0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1] },
},
forms: {
1: [{ strike: ['a', 'x']}, ' ', 'b'],
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different strike examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
s1: { symbol: 'strike', color: [0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1] },
s2: { symbol: 'strike', style: 'forward', color: [0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1] },
},
forms: {
// Array definition
1: [{ strike: ['a', 's1']}, ' ', 'b'],
// Object definition
2: {
strike: {
content: ['a', '_ + ', 'b'],
symbol: 's1',
},
},
// Additional options to make strike overhang more
3: {
strike: {
content: ['a', 'b'],
symbol: 's1',
topSpace: 0.2,
rightSpace: 0.2,
leftSpace: 0.2,
bottomSpace: 0.2,
},
},
// Forward strike
4: { strike: [['a', '_ +', 'b'], 's2'] },
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Box
Equation box

Place a EQN_BoxSymbol around an equation phrase
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string
- inSize: boolean | undefined = false
falseexcludes box symbol from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined = 0
space between box symbol and content on the left, right, bottom and top sides
- topSpace: number | undefined = space
use when top space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - rightSpace: number | undefined = space
use when right space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - bottomSpace: number | undefined = space
use when bottom space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - leftSpace: number | undefined = space
use when left space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { box: ['a', 'box', true, 0.1] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different box examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
box: { symbol: 'box' },
},
forms: {
// Array equation
1: ['a', { box: ['b', 'box'] }, 'c'],
// Object definition
2: {
box: {
content: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
symbol: 'box',
},
},
// Additional options for layout
3: {
box: {
content: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
symbol: 'box',
space: 0.2,
},
},
// Box is included in the layout spacing
4: [
'a',
{
box: {
content: 'b',
symbol: 'box',
space: 0.2,
inSize: true,
},
},
'c'
],
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_TouchBox
Equation touch box
Place a box symbol around an equation phrase
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string
- space: number | undefined = 0
space between box symbol and content on the left, right, bottom and top sides
- topSpace: number | undefined = space
use when top space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - rightSpace: number | undefined = space
use when right space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - bottomSpace: number | undefined = space
use when bottom space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty - leftSpace: number | undefined = space
use when left space between content and box should be different thant
spaceproperty
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Bar
Equation bar
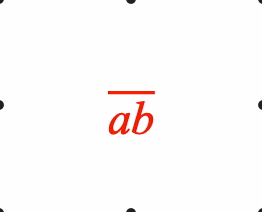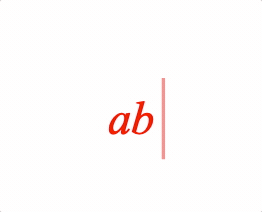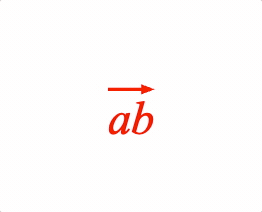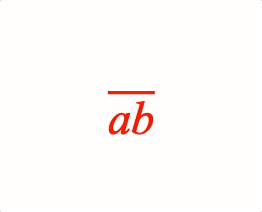
Place a bar (or bracket) symbol to the side of an equation phrase.
Symbols that can be used with bar are:
- EQN_BarSymbol
- EQN_ArrowSymbol
- EQN_BraceSymbol
- EQN_BracketSymbol
- EQN_SquareBracketSymbol
- EQN_AngleBracketSymbol
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes box symbol from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined = 0.03
space between content and the symbol
- overhang: number | undefined = 0
amount symbol extends beyond content
- length: number | undefined = overrides overhang
total length of symbol
- left: number | undefined = overrides overhang and length, and only for side 'top' or 'bottom'
amount symbol extends beyond content to the left
- right: number | undefined = overrides overhang and length, and only for side 'top' or 'bottom'
amount symbol extends beyond content to the right
- top: number | undefined = overrides overhang and length, and only for side 'left' or 'right'
amount symbol extends beyond content to the top
- bottom: number | undefined = overrides overhang and length, and only for side 'left' or
'right'
amount symbol extends beyond content to the bottom
- side: 'left' | 'right' | 'top' | 'bottom' | undefined = top
- minContentHeight: number | undefined
custom min content height for auto symbol sizing when side is
'top'or'bottom' - minContentDescent: number | undefined
custom min content descent for auto symbol sizing when side is
'top'or'bottom' - minContentAscent: number | undefined
custom min content ascent for auto symbol sizing when side is
'top'or'bottom' - descent: number | undefined
force descent of symbol when side is
'top'or'bottom'- height is forced withlengthproperty - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
bar: { symbol: 'bar', side: 'top' },
},
forms: {
1: { bar: ['a', 'bar', 'top'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different bar examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
hBar: { symbol: 'bar', side: 'top' },
vBar: { symbol: 'bar', side: 'right' },
hArrow: { symbol: 'arrow', direction: 'right' },
},
forms: {
// Array equation
1: { bar: [['a', 'b'], 'hBar', 'top'] },
// Object definition
2: {
bar: {
content: ['a', 'b'],
symbol: 'hBar',
side: 'bottom',
},
},
// Additional options for layout
3: {
bar: {
content: ['a', 'b'],
symbol: 'vBar',
side: 'right',
overhang: 0.1,
},
},
// Vector arrow
4: {
bar: {
content: ['a', 'b'],
symbol: 'hArrow',
side: 'top',
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Integral
Equation integral
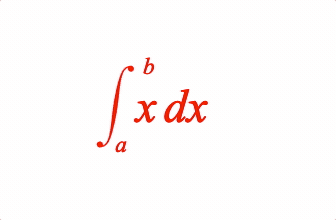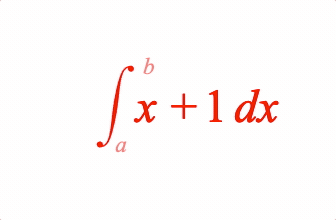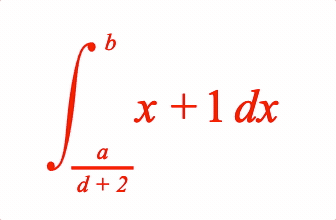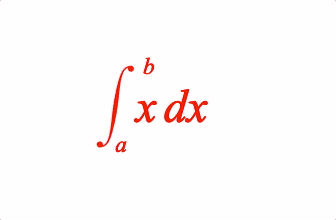
Place an integral (with optional limits) before an equation phrase
Use with a EQN_IntegralSymbol symbol.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below.
Properties
- symbol: string
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- from: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
bottom limit
- to: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
top limit
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes box symbol from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined = 0.05
horizontal space between symbol and content
- topSpace: number | undefined = 0.1
space between content top and symbol top
- bottomSpace: number | undefined = 0.1
space between content bottom and symbol bottom
- height: number | undefined
force height of symbol
- yOffset: number | undefined = 0
y offset of symbol
- scale: number | undefined = 1
content scale
- fromScale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of *from* (bottom) limit
- toScale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of *to* (top) limit
- fromOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = side:
[0, 0], topBottom: [0, -0.04], topBottomCenter: [0, -0.04]
from limit offest
- toOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = side: [0, 0]
topBottom: [0, 0.04], topBottomCenter: [0, 0.04]
to limit offest
- limitsPosition: 'side' | 'topBottom' | 'topBottomCenter' | undefined = 'side'
limits relative to symbol.
sideis to the right of the symbol ends,topBottomis above and below the symbol ends andtopBottomCenteris above and below the integral mid point - limitsAroundContent: boolean | undefined
falsemeans content left is aligned with furthest right of limits - fromXPosition: 'left' | 'center' | 'right' | number | undefined = side: 0.5, topBottom: 0.1,
topBottomCenter: 'center'
x position of limit relative to the symbol
- fromYPositio: 'bottom' | 'top' | 'middle' | 'baseline' | number | undefined = 'bottom'
y position of the limit relavite to the symbol
- fromXAlign: 'left' | 'center' | 'right' | number | undefined = side: 'left', topBottom: center,
topBottomCenter: 'center'
limit x alignment
- fromYAlign: 'bottom' | 'top' | 'middle' | 'baseline' | number | undefined = side: 'middle', topBottom: 'top',
topBottomCenter: 'top'
limit y alignment
- toXPosition: 'left' | 'center' | 'right' | number | undefined = side: 'right', topBottom: 0.9,
topBottomCenter: 'center'
x position of limit relative to the symbol
- toYPosition: 'bottom' | 'top' | 'middle' | 'baseline' | number | undefined = side: 'top',
topBottom: top, topBottomCenter: 'top'
y position of the limit relavite to the symbol
- toXAlign: 'left' | 'center' | 'right' | number | undefined = side: 'left', topBottom: center,
topBottomCenter: 'center'
limit x alignment
- toYAlign: 'bottom' | 'top' | 'middle' | 'baseline' | number | undefined = side: 'middle', topBottom: bottom,
topBottomCenter: 'bottom'
limit y alignment
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { int: ['int', 'x dx', 'a', 'b'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Example showing different integral options
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
i: { symbol: 'int' },
// ic: { symbol: 'int', num: 1, type: 'line' },
},
formDefaults: { alignment: { fixTo: 'x' } },
forms: {
// Root object form
1: {
int: {
symbol: 'i',
content: ['x', ' ', 'dx'],
from: 'a',
to: 'b',
},
},
// Root array form
2: { int: ['i', ['x', ' ', '+', ' ', '_1', ' ', 'dx'], 'a', 'b'] },
// Indefinite tripple integral
3: { int: ['i', ['x', ' ', '+', ' ', '_1', ' ', 'dx']] },
// Custom spacing
4: {
int: {
symbol: 'i',
content: ['x', ' ', '+', ' ', '_1', ' ', 'dx'],
to: 'b',
from: { frac: ['a', 'vinculum', 'd + 2'] },
topSpace: 0.2,
bottomSpace: 0.2,
limitsAroundContent: false,
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_SumOf
Equation sum of
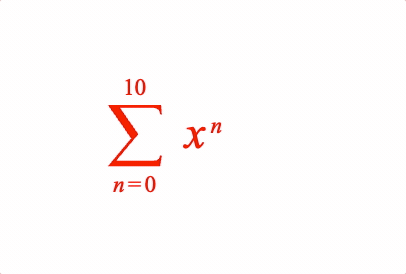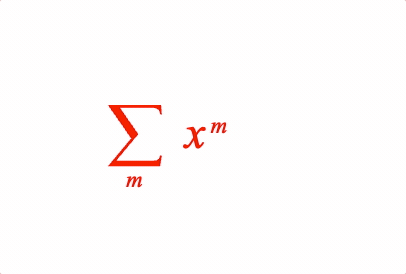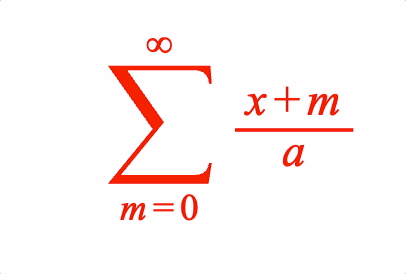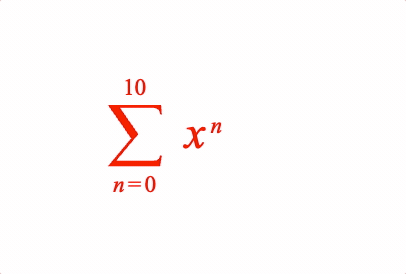
Place an equation phrase in a sum of operation with the symbol EQN_SumSymbol.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- symbol: string
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- from: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
- to: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes sum of operator from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined = 0.1
horiztonaly space between symbol and content
- topSpace: number | undefined = 0.07
space symbol extends above content top
- bottomSpace: number | undefined = 0.07
space symbol extends below content bottom
- height: number | undefined
force height of symbol overwriting
topSpace - yOffset: number | undefined = 0
offset of symbol in y
- scale: number | undefined = 1
content scale
- fromScale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of *from* phrase
- toScale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of *to* phrase
- fromSpace: number | undefined = 0.04
space between symbol and
fromphrase - toSpace: number | undefined = 0.04
space between symbol and
tophrase - fromOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of
fromphrase - toOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of
tophrase - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { sumOf: ['sum', 'x', 'b', 'a'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Example showing different options
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
s: { symbol: 'sum', draw: 'dynamic' },
inf: '\u221e',
},
forms: {
// Object form
1: {
sumOf: {
symbol: 's',
content: [{ sup: ['x', 'n'] }],
from: ['n_1', ' ', '=', ' ', '_0'],
to: '_10',
},
},
// Array form
2: { sumOf: ['s', [{ sup: ['x', 'm'] }], 'm_1', null]},
// Styling with options
3: {
sumOf: {
symbol: 's',
content: { frac: [['x', ' ', '+', ' ', 'm'], 'vinculum', 'a'] },
from: ['m_1', ' ', '=', ' ', '_0'],
to: 'inf',
fromScale: 0.8,
toScale: 0.8,
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_ProdOf
Place an equation phrase in a product of operation with the symbol EQN_ProdSymbol.
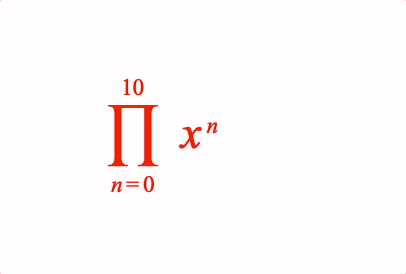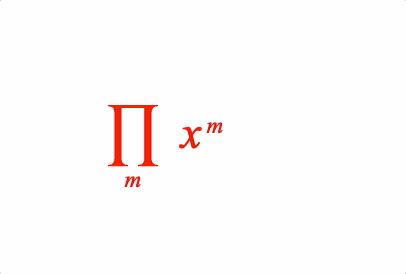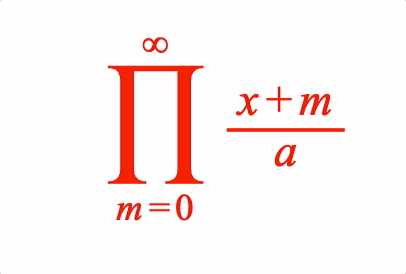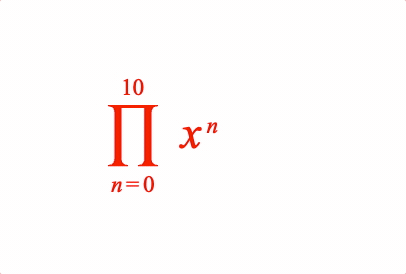
Place an equation phrase in a product of operation
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- symbol: string
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- from: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
- to: TypeEquationPhrase | undefined
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes product of operator from size of resulting phrase - space: number | undefined = 0.1
horiztonaly space between symbol and content
- topSpace: number | undefined = 0.07
space symbol extends above content top
- bottomSpace: number | undefined = 0.07
space symbol extends below content bottom
- height: number | undefined
force height of symbol overwriting
topSpace - yOffset: number | undefined = 0
offset of symbol in y
- scale: number | undefined = 1
content scale
- fromScale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of *from* phrase
- toScale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of *to* phrase
- fromSpace: number | undefined = 0.04
space between symbol and
fromphrase - toSpace: number | undefined = 0.04
space between symbol and
tophrase - fromOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of
fromphrase - toOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of
tophrase - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { prodOf: ['prod', 'x', 'b', 'a'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Example showing different options
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
p: { symbol: 'prod', draw: 'dynamic' },
inf: '\u221e',
},
forms: {
// Object form
1: {
prodOf: {
symbol: 'p',
content: [{ sup: ['x', 'n'] }],
from: ['n_1', ' ', '=', ' ', '_0'],
to: '_10',
},
},
// Array form
2: { prodOf: ['p', [{ sup: ['x', 'm'] }], 'm_1', null]},
// Styling with options
3: {
prodOf: {
symbol: 'p',
content: { frac: [['x', ' ', '+', ' ', 'm'], 'vinculum', 'a'] },
from: ['m_1', ' ', '=', ' ', '_0'],
to: 'inf',
fromScale: 0.8,
toScale: 0.8,
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Subscript
Equation subscript
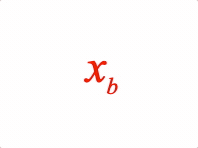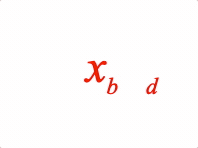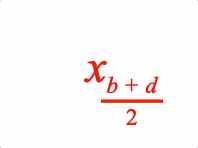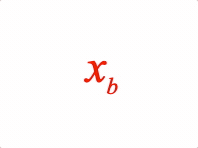
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- subscript: TypeEquationPhrase
- scale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of subscript
- offset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of subscript
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
trueexcludes subscript from size of resulting phrase
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { sub: ['x', '_2'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Example showing different subscript options
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
// Object form
1: {
sub: {
content: 'x',
subscript: 'b',
},
},
// Array form
2: [{ sub: ['x', 'b'] }, ' ', { sub: ['y', 'd'] }],
3: { sub: ['x', ['b', ' ', '+', ' ', 'd']] },
// Subscript offset to adjust layout to keep animation smooth
4: {
sub: {
content: 'x',
subscript: { frac: [['b', ' ', '+', ' ', 'd'], 'vinculum', '_2'] },
offset: [-0.025, -0.02],
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Superscript
Equation superscript
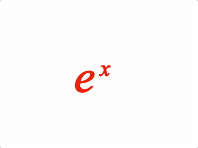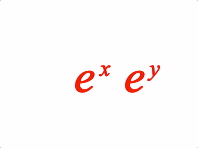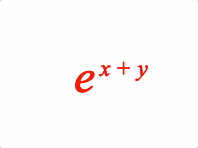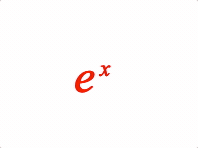
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- superscript: TypeEquationPhrase
- scale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of superscript
- offset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of superscript
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
trueexcludes superscript from size of resulting phrase
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { sup: ['e', 'x'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Examples of superscript animations
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
// Object form
1: {
sup: {
content: 'e',
superscript: 'x',
},
},
// Array form
2: [{ sup: ['e', 'x'] }, ' ', { sup: ['e_1', 'y'] }],
3: { sup: ['e', ['x', ' ', '+', ' ', 'y']] },
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_SuperscriptSubscript
Equation superscript and subscript
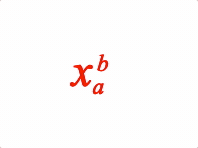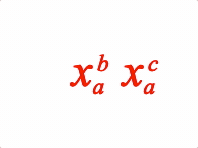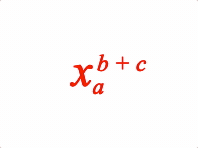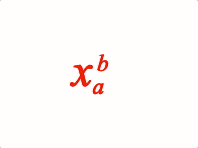
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- superscript: TypeEquationPhrase
- subscript: TypeEquationPhrase
- scale: number | undefined = 0.5
scale of superscript
- superscriptOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of superscript
- subscriptOffset: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0, 0]
offset of subscript
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
trueexcludes superscript from size of resulting phrase
Simple
figure.add({
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { supSub: ['x', 'b', 'a'] },
},
});
Example showing different super-sub script options
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
// Object form
1: {
supSub: {
content: 'x',
superscript: 'b',
subscript: 'a',
},
},
// Array form
2: [{ supSub: ['x', 'b', 'a'] }, ' ', { supSub: ['x_1', 'c', 'a_1'] }],
3: { supSub: ['x', ['b', ' ', '+', ' ', 'c'], 'a'] },
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Comment
Equation comment options used with topComment and bottomComment
functions.
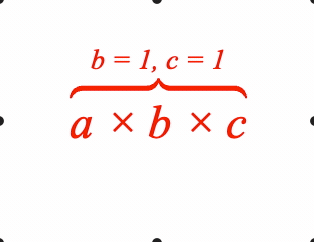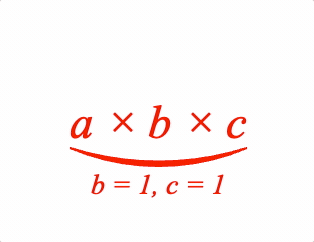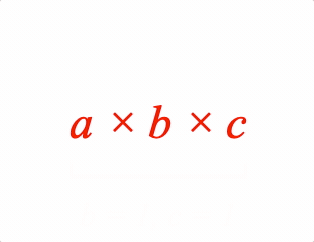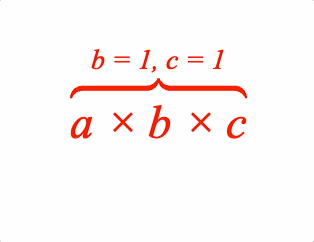
A symbol between the content and comment is optional.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- comment: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string | undefined
optional symbol between content and comment
- contentSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space from content to symbol
- commentSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space from symbol to comment
- contentLineSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space between a line symbol and content
- commentLineSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space between a line symbol and comment
- scale: number | undefined = 0.6
comment scale
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes the symbol and comment from thre resulting size of the equation phrase - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: { topComment: ['radius', 'r = 1'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different comment examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
bBkt: { symbol: 'bracket', side: 'bottom' },
tBrc: { symbol: 'brace', side: 'top' },
bSqr: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'bottom' },
},
forms: {
// Array equation
1: { topComment: ['a \u00d7 b \u00d7 c', 'b = 1, c = 1', 'tBrc'] },
// Object definition
2: {
bottomComment: {
content: 'a \u00d7 b \u00d7 c',
symbol: 'bBkt',
comment: 'b = 1, c = 1',
},
},
// Additional options for layout
3: {
bottomComment: {
content: 'a \u00d7 b \u00d7 c',
symbol: 'bSqr',
comment: 'b = 1, c = 1',
contentSpace: 0.1,
commentSpace: 0.1,
scale: 0.7,
},
},
// Just comment
4: {
bottomComment: {
content: 'a \u00d7 b \u00d7 c',
comment: 'for a > 3',
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_StrikeComment
Equation strike with comment options used with topStrike and bottomStrike
functions.

Use with EQN_Strike symbol.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- symbol: string
strike symbol
- comment: TypeEquationPhrase
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
falseexcludes the symbol and comment from thre resulting size of the equation phrase - space: number | undefined = 0.03
top, right, bottom and left extension of symbol beyond content
- scale: number | undefined = 0.6
comment scale
- commentSpace: number | undefined = 0.03
space from symbol to comment
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
x: { symbol: 'strike', color: [0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1] },
},
forms: {
1: { topStrike: ['radius', 'x', 'radius = 1'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different strike examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
s1: { symbol: 'strike', style: 'forward', color: [0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1] },
},
forms: {
// Array equation
1: { topStrike: ['radius', 's1', 'radius = 1'] },
// Object definition
2: {
bottomStrike: {
content: 'radius',
symbol: 's1',
comment: 'radius = 1',
},
},
// Additional options for layout
3: {
bottomStrike: {
content: 'radius',
comment: 'radius = 1',
symbol: 's1',
scale: 0.8,
space: 0.1,
commentSpace: 0.01,
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Pad
Equation padding options.
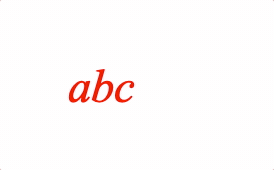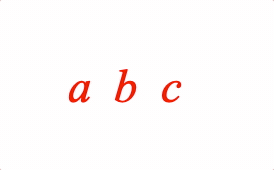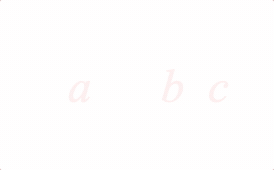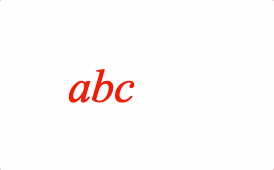
Pads the size of the equation phrase with space.
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- top: number | undefined = 0
- right: number | undefined = 0
- bottom: number | undefined = 0
- left: number | undefined = 0
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
1: ['a', { pad: ['b', 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1] }, 'c'],
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different padding examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
// No padding
1: ['a', 'b', 'c'],
// Array form
2: ['a', { pad: ['b', 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1] }, 'c'],
// Object form
3: [
'a',
{
pad: {
content: 'b',
left: 0.3,
right: 0.1,
},
},
'c',
],
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Matrix
Equation matrix
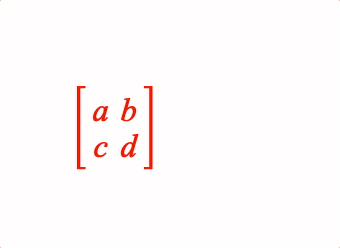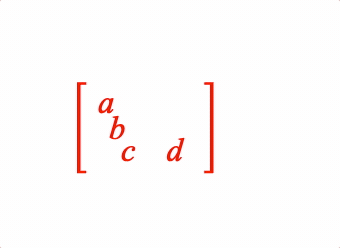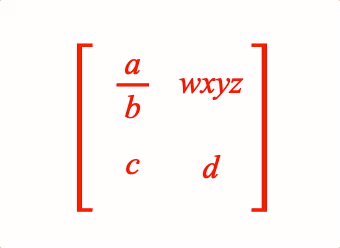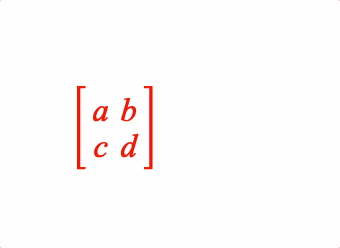
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
Properties
- order: [number, number] | undefined = [1, length-of-content]
- left: string | undefined
left bracket symbol
- content: Array<TypeEquationPhrase> | undefined
Array of equation phrases where each element is a matrix element
- right: string | undefined
right bracket symbol
- scale: number | undefined = 0.7
scale of matrix elements
- fit: 'max' | 'min' | TypeParsablePoint | undefined = 'min'
cell size -
mineach cell is a rectangle with width equal to largest width in its column, and height equal to largest height in its row -maxall cells are a square with dimension equal to the largest dimension of the largest cell -pointall cells are a rectangle with width as point.x and height as point.y - note -maxandpointonly work withyAlign='middle' - space: TypeParsablePoint | undefined = [0.05, 0.05]
space between each cell
- yAlign: 'baseline' | 'middle' | undefined = baseline
align cells in a row with the text baseline, or middle of the cell
- brac: EQN_Bracket | undefined = {}
bracket options not including the symbols
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content
Simple
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
lb: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'left' },
rb: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'right' },
},
forms: {
1: { matrix: [[2, 2], 'lb', ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'rb'] },
},
});
figure.elements._eqn.showForm('1');
Some different equation examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
lb: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'left' },
rb: { symbol: 'squareBracket', side: 'right' },
v: { symbol: 'vinculum' },
},
phrases: {
f: { frac: ['a', 'v', 'b'] },
},
forms: {
// Array equation 2x2 matrix
1: { matrix: [[2, 2], 'lb', ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'rb'] },
// Object definition vector
2: {
matrix: {
content: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'],
left: 'lb',
right: 'rb',
order: [1, 4],
},
},
// Additional options for layout
3: {
matrix: {
content: ['f', 'wxyz', 'c', 'd'],
symbol: 'bSqr',
left: 'lb',
right: 'rb',
order: [2, 2],
},
},
// Fixed size matrix cells
4: {
matrix: {
content: ['f', 'wxyz', 'c', 'd'],
symbol: 'bSqr',
left: 'lb',
right: 'rb',
order: [2, 2],
fit: [0.2, 0.2],
yAlign: 'middle',
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3', '4']
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Lines
Equation lines.
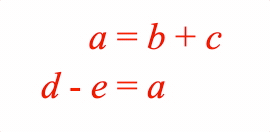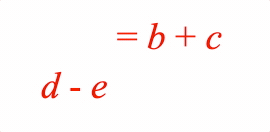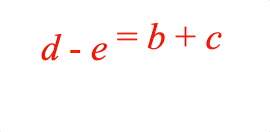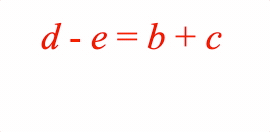
Options can be an object, or an array in the property order below
The equation lines function can split an equation into multiple lines. This might be because one line is too long, or it might be convenient to display different forms of the same equation simultaneously on different lines and then animate between them.
Lines can be justified to the left, center or right, or lines can be aligned
with a specific element from each line (for instance an equals sign). To
justify to a specific element, use justify: 'element' and then define the
element name in the justify property of each line.
Lines can be aligned in y with either the top most part of the top line, the bottom most part of the bottom line, the middle of the lines or any of the line's baselines.
Spacing between lines is defined as either the space between the lowest point (descent) of one line to the highest point (ascent) of the next, or as the space between line baselines.
Properties
- content: Array<EQN_Line | TypeEquationPhrase>
Array of equation phrases or equation line objects
- justify: 'left' | 'center' | 'right' | 'element' | undefined = 'left'
how to align the lines in x. Use 'element' to align the lines with a specific element from each line (that is defined with the
justifyproperty in each line) - baselineSpace: number | null | undefined
default space between baselines of lines. If not
nullthen will overridespace(null). - space: number | undefined
default space between descent of one line and ascent of the next line (
0). - yAlign: 'bottom' | 'middle' | 'top' | number | undefined = 0
How to align the lines in y.
numbercan be any line index, and it will align the baseline of that line. So, using0will align the first line's baseline. - fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content
Two lines, array definition
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
forms: {
0: {
lines: [
[
['a', '_ = ', 'b', '_ + _1', 'c', '_ - _1', 'd'],
['_ + _2', 'e', '_ - _2', 'f'],
],
'right',
0.2,
],
},
},
});
Two lines animating to 1
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
equals1: ' = ',
equals2: ' = ',
},
forms: {
0: {
lines: {
content: [
{
content: ['a_1', 'equals1', 'b', '_ + ', 'c'],
justify: 'equals1',
},
{
content: ['d', '_ - ', 'e', 'equals2', 'a_2'],
justify: 'equals2',
},
],
space: 0.08,
justify: 'element',
},
},
1: ['d', '_ - ', 'e', 'equals1', 'b', '_ + ', 'c'],
},
});
figure.getElement('eqn').showForm(0);
figure.getElement('eqn').animations.new()
.goToForm({
delay: 1, target: '1', duration: 1, animate: 'move',
})
.start();
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
EQN_Annotate
Equation annotation
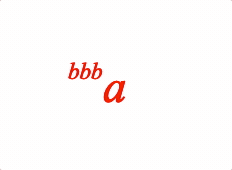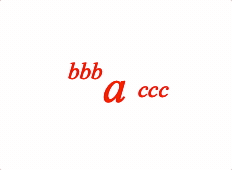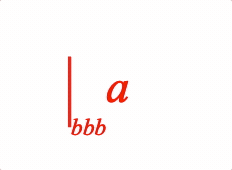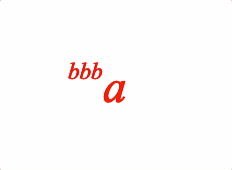
An annotation is an equation phrase ('annotation') which is laid out relative to another equation phrase ('content'). For example:
AAAA
AAAA
CCCCCCCC
CCCCCCCC
CCCCCCCC
CCCCCCCC
The options for defining how to annotate one equation phrase with another is EQN_Annotation
Content can also be annotated with a glyph (that itself may also be annotated). The glyph can either encompass the content, or can be to the top, bottom, left or right of the content
Top Glyph
GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG
GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG Encompassing Glyph
/
/
GGG GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG GGG
GGG GGG GGG GGG
GGG GGG CCCCCCC GGG GGG
Left GGG GGG CCCCCCC GGG GGG Right
Glyph GGG GGG CCCCCCC GGG GGG Glyph
GGG GGG GGG GGG
GGG GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG GGG
GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG
GGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG
Bottom Glyph
This function is used internally by almost all equation functions (except for fraction) for their layout. As such, it is very generic and powerful. It should also almost never neeed to be used as most layouts can be achieved with a different functions that will have more succinct code that is more readable.
This is provided so all layout corner cases not covered by the functions above are possible - including with custom glyphs.
Options can only be an object.
Properties
- content: TypeEquationPhrase
- annotation: EQN_Annotation | undefined
use for just one annotation
- annotations: Array<EQN_Annotation> | undefined
use for multiple annotations
- inSize: boolean | undefined = true
truemeans resulting size includes annotations - space: number | undefined = 0
extend resulting equation phrase size by space on top, right, bottom and left sides
- topSpace: number | undefined
extend resulting equation phrase size by space on top
- bottomSpace: number | undefined
extend resulting equation phrase size by space on bottom
- leftSpace: number | undefined
extend resulting equation phrase size by space on left
- rightSpace: number | undefined
extend resulting equation phrase size by space on right
- contentScale: number | undefined = 1
scale content
- glyphs: EQN_Glyphs | undefined
glyphs to annotate content with
- fullContentBounds: boolean | undefined = false
use full bounds of content, overriding any
inSize=falseproperties in the content - useFullBounds: boolean | undefined = false
make the bounds of this phrase equal to the full bounds of the content even if
fullContentBounds=falseand the brackets only surround a portion of the content
Some different annotation examples
figure.add({
name: 'eqn',
make: 'equation',
elements: {
bar: { symbol: 'bar', side: 'right' },
},
forms: {
// Single annotation
1: {
annotate: {
content: 'a',
annotation: {
content: 'bbb',
yPosition: 'top',
yAlign: 'bottom',
xPosition: 'left',
xAlign: 'right',
scale: 0.5,
},
},
},
// Multiple annotations
2: {
annotate: {
content: 'a',
annotations: [
{
content: 'bbb',
yPosition: 'top',
yAlign: 'bottom',
xPosition: 'left',
xAlign: 'right',
scale: 0.5,
},
{
content: 'ccc',
xPosition: 'right',
yPosition: 'middle',
xAlign: 'left',
yAlign: 'middle',
scale: 0.5,
offset: [0.05, 0],
},
],
},
},
// With glyph
3: {
annotate: {
content: 'a',
glyphs: {
left:{
symbol: 'bar',
overhang: 0.1,
annotation: {
content: 'bbb',
xPosition: 'right',
yPosition: 'bottom',
xAlign: 'left',
yAlign: 'middle',
scale: 0.5,
},
},
},
},
},
},
formSeries: ['1', '2', '3'],
});
const eqn = figure.elements._eqn;
eqn.onClick = () => eqn.nextForm();
eqn.setTouchable();
eqn.showForm('1');
To test examples, append them to the boilerplate
- fit width, ascent and descent to either match width, height or fully contain the content